The hype surrounding Pokémon Go has shown that virtual realities can influence and enrich the real world. Whether with the help of data glasses or as an app on a smartphone or tablet, Pokémon Go’s technology called “Augmented Reality” could become one of the big innovations of the coming years, not only in the entertainment industry. Augmented Reality also promises new possibilities for in-company education to support and train employees in their work. But what is Augmented Reality and what potential is really visible for this technology? The editors of the eLearning Journal try to give initial answers to these questions.
The term Augmented Reality refers to the enrichment of the real world with digital or virtual content. Augmented Reality is often understood as the representation of information by fading in or superimposition into the real world, i.e. computer-generated additional information, for example in the form of text, images or videos, is projected into the visual image of the wearer with the aid of data glasses (e.g. Google Glass) or via app on a tablet or smartphone. Thus Augmented Reality differs clearly from the related technology of Virtual Reality in its approach. While Virtual Reality learners can immerse themselves in high-quality simulations and experience a multitude of situations realistically in computer-generated space, Augmented Reality impresses with the enrichment of reality with digital information.
Augmented Reality in in-company training
Due to this strength, one of the interesting areas of application of this technology is performance support. With performance support, employees are to be supported directly in the work process with demand-orientated assistance in the need of a concrete problem, so-called „moment of need“. This is especially true when it comes to orientation in space or the circumference of machines. Augmented Reality is therefore particularly suitable for maintenance, repair and service work, for example, because data glasses can be used to display helpful information directly in the field of view for a technician, e.g. in case of a machine, using data goggles, thus supporting the work process. Augmented Reality works similarly with smartphones or tablets. These can, for example, recognize components of an engine and automatically display specifications stored for the technician. In the logistics industry, employees can use Augmented Reality to project unloading areas and directional information directly into the field of vision, for example, making the workflow easier and more efficient.
Increasing relevance of Augmented Reality in the coming years
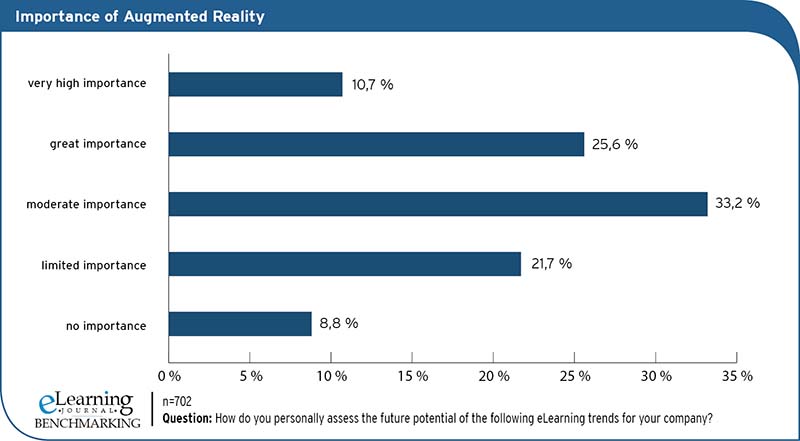
Similar to Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality is also quasi irrelevant in the everyday life of in-company education in German-speaking countries. The few concrete application examples are usually either pilot projects, in order to explore the possibilities of the technology, or owed to a very concrete and company-dependent need, which cannot easily be transferred to the broad masses. At the same time, technology is still relatively new and with increasing experience, it should be possible to eradicate childhood diseases and define areas of application in the future, both on the supplier and on the user side. The results of the eLearning BENCHMARKING Study 2017 show that there is potential for Augmented Reality. 36.3 % of the study participants rate AR as very important (10.7 %) or important (25.6 %) for their own company in the future. In addition, a large majority see at least a certain future relevance for their own company, as only 8.8 % of the study participants stated that in their view this technology will have no significance in the future. The results of the mmb Trend Monitor 2017 confirm this assessment of the potential of Augmented Reality for the coming years. Also in the survey of the mmb institute, 33% oft he surveyed experts confirmed that AR is of central importance as a form of learning for in-company learning in the next three years.
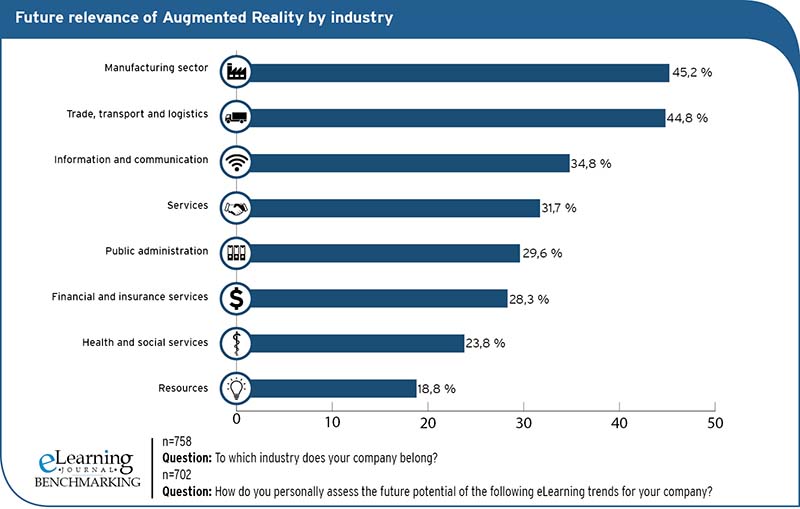
AR is particularly interesting for trade, transport and logistics as well as the manufacturing industry
If one compares the expectations of Augmented Reality between different industries, there are sometimes clear differences in the assessment of the future relevance of the industry. The largest potential for AR, at 45.2 %, is seen in the manufacturing industry. At 44.8 %, companies in the trade, transport or logistics sector have almost the same expectations. On the other hand, the subject of AR is seen much more soberly in the resources sector, since only 18.8
of the study participants of these companies rate the method as very important or important. A similar picture emerges when looking at the number of study participants who regard Augmented Reality as completely unimportant. The figures for manufacturing (5.2%) and trade, transport and logistics (4.8%) are again among the lowest of all sectors. Interestingly, the comparative value in the information and communications industry is even significantly lower at 2.2. This means that the overwhelming majority of information and communication companies seem to regard the topic of AR somewhere between important and rather unimportant. At 25% and 18.5%, the resource sector and public administrations are particularly critical of Augmented Reality and rate the technology by far the most unimportant. All in all, these values seem to support the hypothesis set out at the beginning, according to which Augmented Reality can represent added value for companies, especially as performance support. The above-average values for the manufacturing industry and for companies from the trade, transport and logistics sector underline the assumption that Augmented Reality can support work processes in dealing with machines and orientation in space and offer uncomplicated solutions to problems.
Forecast
Currently, Augmented Reality in in–company training is still largely a novelty in German-speaking countries. Nevertheless, the technology for training and further education in companies does not seem to be uninteresting in principle. Augmented Reality could have real growth potential in the coming years, especially in the manufacturing industry and in the trade, transport and logistics sectors.





